Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University
DISCIPLINE: PULMONOLOGY
PAPER: OSPE (Ten stations)
Q.1. How will you counsel a 28 years old male patient who will receive CAT-Il anti-TB drugs for smear positive PTB?
Checklist:
|
Greetings & self-introduction |
0.5 |
|
Discussion about disease |
1.0 |
|
Discussion about drug |
1.0 |
|
Indication: why prescribed |
1.0 |
|
Side effects |
1.0 |
|
Assurance about side effects |
1.0 |
|
Duration of treatment and time of follow up |
1.0 |
|
Where will you get drugs/DOT |
1.0 |
|
What will happen if there is incomplete treatment |
1.0 |
|
Aware about use of mask |
0.5 |
|
Feedback |
1.0 |
Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University
DISCIPLINE: PULMONOLOGY
PAPER: OSPE (Ten stations)
Q.2. Show the procedure of correct use of metered dose inhaler (MDI) with and without spacer and spacer with mask to an asthma patient?
- Correct use of MDI…………………………………………………………….6
- Shake and position of device in between thumb and index finger
- Exhale
- Place the mouth piece in between lips
- Coordination in between deep inspiration and pressure over canester
- Hold the breath for 10 sec, wash mouth after using device.
- Repeat the procedure after 2 minutes interval
- Correct use of spacer ………………………………………………………..3
- Shake the device
- Fixed with spacer
- 1 puff and 5 times breathing in spacer.
- Hold the breath 4 to 10 sec during inspiration.
- Repeat it for next puff .
- Use of spacer with mask …………………………………………………..1
Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University
COURSE: DTCD
DISCIPLINE: PULMONOLOGY
PAPER: OSPE (Ten stations)
Q.3. A 30 year old man known case of right middle lobe bronchiectasis admitted in your unit with massive haemoptysis. Previously he was admitted in local hospital three times for recurrent infective exacerbation . How will you manage him?
Checklist:
|
Initial management with A, B and C (Air way , Breathing and Circulation : I/V channel open , Blood grouping ) |
2.0 |
|
Advice regarding posture of the patient |
1.0 |
|
Discussion about medical management : 1) Control of infection 2) Postural drainage (contraindicated) |
2.0 |
|
Discussion about surgical management |
2.0 |
|
If surgical intervention not possible (eg. Bronchial artery embolization). |
1.0 |
|
Vaccination |
2.0 |
Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University
DISCIPLINE: PULMONOLOGY
PAPER: OSPE (Ten stations)
Q.4. Look at the picture- This man came in OPD with the complain of cough , left sided chest pain and recurrent haemoptysis for two months .

- What are the findings of the above pictorial?................................................................2
- Partial ptosis
- Miosis
- Enopthalmus
- Is there any name of this clinical presentation? What are the other components of this presentation ?................................................................................................................2
Horner’s Syndrome . Anhydrosis .
- What may be the underlying cause?................................................................................3
Left sided bronchial carcinoma .
- What is the possible site of lesion?.................................................................................2
Involvement of left sided sympathetic chain .
- Mention two important investigations for this patient. ..................................................1
CT scan of chest , CT guided FNAC and Fiber optic bronchoscope (FOB)
Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University
DISCIPLINE: PULMONOLOGY
PAPER: OSPE (Ten stations)
Q.5.This is an X-ray chest P-A view of 35 years old man who presented with fever, cough and occasional scanty haemoptysis for one month. There was a cavitary lesion in right upper zone .
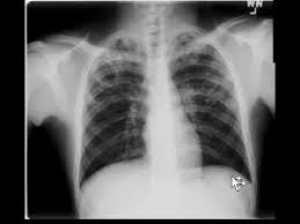
- What is your diagnosis ? Describe the X-ray . .........................................................................3
PTB (Bilateral) . Bilateral patchy opacity involving upper zones with a cavitary lesion in right side.
- What are the other causes of cavitary lung lesion ?...............................................................2
Infective : MTB, NTM , bacterial, fungal . Vasculitis : WG, RA. Neoplastic : bronchial carcinoma . Non –hodgkins lymphoma .
- What are the radiological signs of active pulmonary tuberculosis ?......................................2
Increasing patchy opacity /soft shadow in serial X-ray , cavitary lesion , pleural effusion etc.
- How will you differentiate malignant cavity from tubercular cavity ?....................................3
Malignant cavity : Thick wall , acentric cavity , minimal fluid , surrounding inflammation absent , irregular inner and outer margin.
Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University
DISCIPLINE: PULMONOLOGY
PAPER: OSPE (Ten stations)
Q.6. Read CT scan of chest.

- What are the findings?..................................................................5X2= 10
- A cavitary lesion with crescentic air shadow in right lung.
- What is the likely diagnosis?
- Aspergilloma.
- Mention the presenting feature.
- Asymptomatic
- Haemoptysis
- What are the treatment options?
- If asymptomatic, no treatment is required.
- If massive/recurrent haemoptysis, surgery.
- Name two treatment options if surgery is not possible.
- Local instillation of Amphotericin B.
- Bronchial artery embolization.
Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University
DISCIPLINE: PULMONOLOGY
PAPER: OSPE (Ten stations)
Q.7. Look at the spirometric reading given below:
|
|
Predicted |
Test |
% Predicted |
Post-bronchodilator |
% Test |
|
FVC |
3.91 |
3.59 |
92.0 |
4.61 |
+28.4 |
|
FEV1 |
3.14 |
1.42 |
45.2 |
2.01 |
+41.7 |
|
FEV1/FVC |
77.3 |
39.5 |
51.1 |
43.6 |
|
- What type of disease it is ?.........................................................................2X5 = 10
- Obstructive airway disease .
- Is the reversibility test positive ? If it is positive, what are the criterias ?
- Positive , FEV1 increase > 200 ml and FEV1> 12 %
- What is your diagnosis ?
COPD with reversibility component (ACOS)
- Draw an expiratory loop of flow volume curve of obstructive air way disease and a restrictive air way disease .
- What is the basic component of management of your possible diagnosis ?
Inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) and bronchodilator.

Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University
DISCIPLINE: PULMONOLOGY
PAPER: OSPE (Ten stations)
Q.8. Look at the picture.

- What is your finding ?.................................................................................................. 5X2 =10
- Dilated veins in upper part of chest .
- What is the most likely diagnosis?
- SVCO.
- What may be the complains of the patient?
Swelling of face and neck , headache, dysphagia, stridor , shortness of breath etc.
- What are the most likely causes of this condition?
Bronchial carcinoma , lymphoma , metastatic mediastina lymphadenopathy, retro-sternal goiter
- How will you investigate the patient ?
- X-ray chest , CT scan of chest , Ct guided FNAC , FOB , EBUS-TBNA.
Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University
COURSE: MD (Pulmonology), Residency Phase-A
DISCIPLINE: PULMONOLOGY
PAPER: OSPE (Ten stations)
Q.9. A patient with very sever COPD came with following ECG .

- Mention three important findings...................................................................5X2 = 10
- Tall p wave in lead II
- Tall R wave in lead V1
- Right axis deviation
- Asymmetrical T wave inversion (strain pattern) in II , III , aVF and V1- V4
- What is the most possible cause?
- COPD with right ventricular hypertrophy due to pulmonary hypertension.
- Patient may have right parasternal heave , what are the other impotant findings may present in precordium ?
Palpable P2 , loud P2 , Pansystolicmurmurin tricuspid area , ejection systolic murmur in pulmonary area .
- How you will manage the case ?
- Optimum management of COPD, LTOT, Diuretic etc .
Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University
DISCIPLINE: PULMONOLOGY
PAPER: OSPE (Ten stations)
Q.10. Look at the transverse section of HRCT of Chest .
- What are the findings of the above HRCT scan? .......................................................... 5X2 = 10
- What is the likely diagnosis?
Bilateral bronchiectasis .
- Mention two important signs of this patient
Bilateral coarse crepitation , altered with cough and clubbing .
- Mention four important presentation of this patient.
Asymptomatic , cough with profuse sputum , haemoptysis ,corpulmonale.
- Mention treatment options of this patient
Postural drainage, control of infection .
Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University
DISCIPLINE: PULMONOLOGY
PAPER: OSPE (Ten stations)
Q. 11) A 62 years old man presented to a pulmonologist with cough for 3 months, shortness of breath for 15 days and having an X-ray chest P-A view , showing left sided opaque hemithorax .
- Describe the bronchoscopic view of this picture ?..................................................5X2 =10
Left sided endobronchial mass lesion completely occluding the lumen of left principal bronchus.
- Is the carina normal ?
Normal and sharp .
- If it is a Non small cell carcinoma, is surgical treatment possible ?
Not possible (as the mass lesion is within 2 cm of carina ) .
- How will you give palliative management for shortness of breath ?
Thermo plasty / Argon plasma coagulation (APC) followed by stenting.
Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University
DISCIPLINE: PULMONOLOGY
PAPER: OSPE (Ten stations)
Q.12) A 60 years old man presented to pulmonologist with persistent dry cough for six months and exortional shortness of breath for three months. The physician found following characteristics in HRCT of chest .
- If there is no etiological factor , what type of ILD it is ?......................................5X2=10
IPF
- Mention the characteristic features in HRCT of chest .
Reticular shadow , subpleural cyst , honey combing , peripheral distribution , less Ground glass opacity(GOO), traction bronchiectasis .
- What physical findings you may get in this patient ?
Cyanosis , clubbing , bilateral fine end inspiratory creps not altered with cough .
- Mention the findings you may get in spirometry, DLCO and six minute walk test .
FEV1/FVC normal or increased , FVC – decreased , DLCO –decreased , SMWT- desaturation


Comments